AviSYBR™
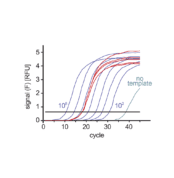
Keep in freezer (≥ -20°C) AviSYBR™ SYBR Green Master Mix PCR is a highly sensitive and user-friendly solution for real-time quantitative analysis of DNA and cDNA targets. This product combines SYBR Green I dye with a dual hot-start Taq polymerase (chemically modified and antibody-mediated) in a pre-optimized buffer solution.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Offers high-quality performance at an affordable price.
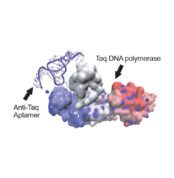
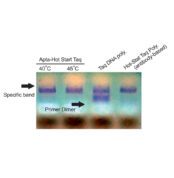
- Advanced Hot-Start Technology: Aptamer-based hot-start Taq DNA polymerase ensures high specificity and prevents non-specific amplification.
- Long-Term Stability: Stable for extended periods, minimizing the need for frequent reagent preparation.
- Ease of Use: Pre-mixed format simplifies reaction setup and reduces pipetting errors.
- Rapid Amplification: Short initial denaturation time allows for faster PCR runs.
AviTooX™
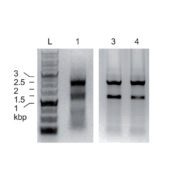
Keep in freezer (≥ -20°C) 2X Taq PCR Master Mix + blue dye AviTooX™ is an all-inclusive solution designed to streamline PCR amplification processes. This convenient mix combines key components such as AviTaq™ (Taq DNA polymerase), reaction buffer, dNTPs mixture, and a protein stabilizer at double concentration for enhanced efficiency and consistent results. Furthermore, AviTooX™ has been optimized for user convenience by incorporating sediment for electrophoresis and a 2X loading dye solution. Notably, this Master Mix demonstrates sustained activity akin to AviTaq™, even at room temperature. It is particularly well-suited for PCR products under 3 Kb.
AviUCiDiNA™
Keep in freezer (≥ -20°C) cDNA Synthesis Kit (Optimum activity at 55 °C) AviUCiDiNA™ contains all necessary components for conversion of total RNA or mRNA to the single stranded cDNA. The 2x Buffer mix solutions contains: RT buffer
1mM dNTP mixture
8mM MgCl2
Oligo d(t)16
Random hexamer
Stabilizer Enzyme mix contains: Thermostable H-minus MMLV with an optimum activity at 55 °C RNase Inhibitor Stabilizer.















































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.